Reputation, Trust and Cooperation
“Tit for Tat”, a strategy in repeated game theoretical interactions, is a prime example to explain how inherent attributes of agents, such as cooperation or defection, shape social behavior. Reputation generates a strong signal for firms and online users to develop trust in information provided by their counterparty.
Related Publications
Should the government reward cooperation? Insights from an agent-based model of wealth redistribution
Advances in Complex Systems - 2021
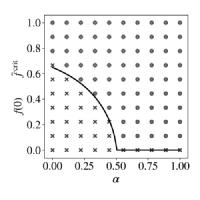
Quantifying the importance of firms by means of reputation and network control
Frontiers in Big Data - 2021
Modeling User Reputation in Online Social Networks: The Role of Costs, Benefits, and Reciprocity
Entropy - 2020
The interdependence of corporate reputation and ownership: A network approach to quantify reputation
Royal Society Open Science - 2019
Understanding Popularity, Reputation, and Social Influence in the Twitter Society
Policy & Internet - 2017
How can social herding enhance cooperation?
ACS - Advances in Complex Systems - 2013
Moving recommender systems from on-line commerce to retail stores
Information Systems and e-Business Management - 2012
Optimal migration promotes the outbreak of cooperation in heterogeneous populations
ACS - Advances in Complex Systems - 2012
A tunable mechanism for identifying trusted nodes in large scale distributed networks
Proceedings of 11th IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (TrustCom 2012) - 2012
Tweetgames: A framework for Twitter-based collaborative social online games
7th International Conference on Collaborative Computing (CollaborateCom 2011), Orlando, FL, USA - 2011

Trust as the basis of coalition formation in electronic marketplaces
ACS - Advances in Complex Systems - 2011
Emotions in product reviews – empirics and models
IEEE International Conference on Privacy, Security, Risk, and Trust, and IEEE International Conference on Social Computing, PASSAT/SocialCom - 2011
Dilemmas of partial cooperation
Evolution - 2010
Impact of aging on the evolution of cooperation in the spatial prisoner's dilemma game
Physical Review E - 2009
Personalised and Dynamic Trust in Social Networks
Proceedings of the third ACM conference on Recommender systems-RecSys '09 - 2009
Coping with information overload through trust-based networks
Managing Complexity: Insights, concepts, Applications - 2008
Alternating cooperation strategies in a route choice game: Theory, experiments, and effects of a learning scenario
Games, Rationality, and Behaviour - 2008
When does defection pay? The stability of institutional arrangements in clusters
Journal of Economic Interaction and Coordination - 2007

Impact of Trust on the Performance of a Recommendation System in a Social Network
Proceedings of the Workshop on Trust at the Fifth International Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems (AAMAS'06) - 2006

