A Weighted Balance Model of Opinion Hyperpolarization
Simon Schweighofer, Frank Schweitzer and David Garcia
Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation (2020)
Research: Opinions Emotions
Abstract
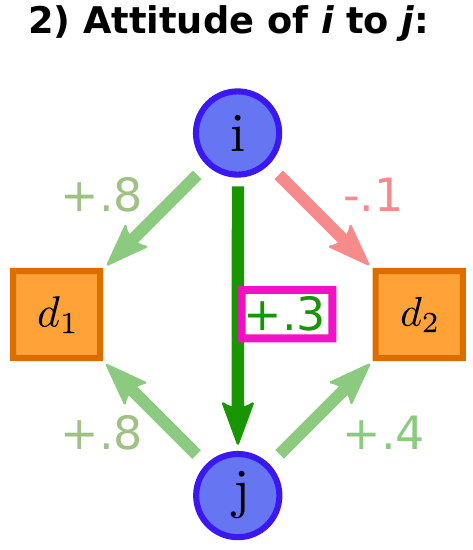
Polarization is threatening the stability of democratic societies. Until now, polarization research has focused on opinion extremeness, overlooking the correlation between different policy issues. We explain the emergence of hyperpolarization, i.e. the combination of extremeness and correlation between issues, by developing Weighted Balance Theory (WBT), a new theory of opinion formation. WBT extends Heider’s cognitive balance theory to encompass multiple weighted attitudes. We validate WBT on empirical data from the 2016 National Election Survey. Furthermore, we develop an opinion dynamics model based on WBT, which, for the first time, is able to generate hyperpolarization and to explain the link between affective and opinion polarization. In addition, our theory encompasses other phenomena of opinion dynamics, including mono - polarization and backfire effects.