How do OSS projects change in number and size? A large-scale analysis to test a model of project growth
Frank Schweitzer, Vahan Nanumyan, Claudio Juan Tessone and Xi Xia
ACS - Advances in Complex Systems (2014)
Research: Software Engineering
Abstract
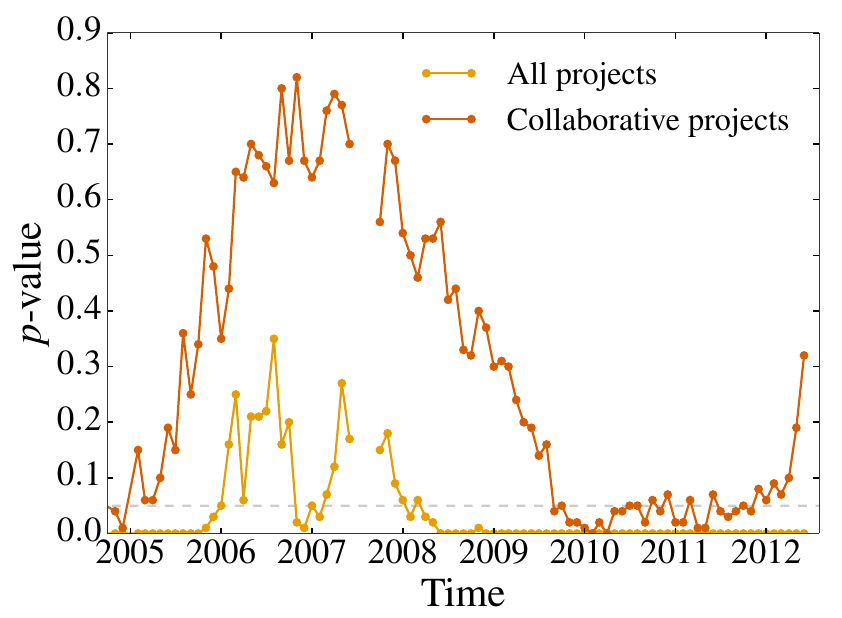
Established open source software (OSS) projects can grow in size if new developers join, but also the number of OSS projects can grow if developers choose to found new projects. We discuss to what extent an established model for firm growth can be applied to the dynamics of OSS projects. Our analysis is based on a large - scale data set from SourceForge (SF) consisting of monthly data for 10 years, for up to 360,000 OSS projects and up to 340,000 developers. Over this time period, we find an exponential growth both in the number of projects and developers, with a remarkable increase of single - developer projects after 2009. We analyze the monthly entry and exit rates for both projects and developers, the growth rate of established projects and the monthly project size distribution. To derive a prediction for the latter, we use modeling assumptions of how newly entering developers choose to either found a new project or to join existing ones. Our model applies only to collaborative projects that are deemed to grow in size by attracting new developers. We verify, by a thorough statistical analysis, that the Yule–Simon distribution is a valid candidate for the size distribution of collaborative projects except for certain time periods where the modeling assumptions no longer hold. We detect and empirically test the reason for this limitation, i.e., the fact that an increasing number of established developers found additional new projects after 2009.